Electric Vehicle Testing
Introduction
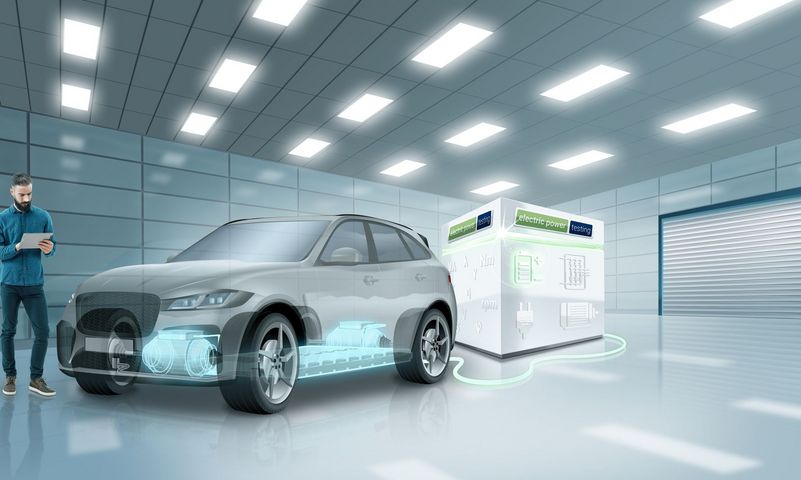
Electric vehicle (EV) testing is a crucial process to ensure the safety, performance, and reliability of electric vehicles. As the adoption of EVs continues to rise, rigorous testing protocols are implemented to meet regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
Types of Testing
1. Battery Testing
- Capacity Testing: Measures the total amount of energy a battery can store.
- Cycle Life Testing: Evaluates how many charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity degrades.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses battery performance under various temperature conditions to ensure safety and efficiency.
2. Range Testing
Determines the maximum distance an EV can travel on a single charge under controlled conditions. This includes highway and city driving simulations to provide accurate range estimates.
3. Safety Testing
- Crash Testing: Ensures the vehicle can protect occupants during collisions.
- Thermal Runaway Testing: Checks for potential overheating and fire hazards in the battery system.
- Water Ingress Testing: Ensures the vehicle’s electrical components are protected from water damage.
4. Performance Testing
- Acceleration and Braking: Measures the vehicle’s acceleration, top speed, and braking efficiency.
- Handling and Stability: Evaluates how the vehicle responds to steering inputs and maintains stability during various driving maneuvers.
Regulatory Standards
EVs must comply with various international standards, such as:
- ISO 26262: Functional safety for road vehicles.
- UNECE Regulation No. 100: Safety requirements for electric powertrains.
- SAE J1772: Electric vehicle and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle conductive charge coupler.
Conclusion
Electric vehicle testing is a multi-faceted process that ensures EVs are safe, efficient, and reliable. By adhering to stringent testing protocols, manufacturers can deliver high-quality vehicles that meet the evolving needs of consumers and regulatory bodies.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Categories
- Car News (4)
- Car Reviews (3)
- Electric Cars (2)
- EV Battery (1)
- EV Charging (3)
- EV Testing (1)
- Uncategorized (1)