The Environmental Benefits of Switching to an Electric Vehicle
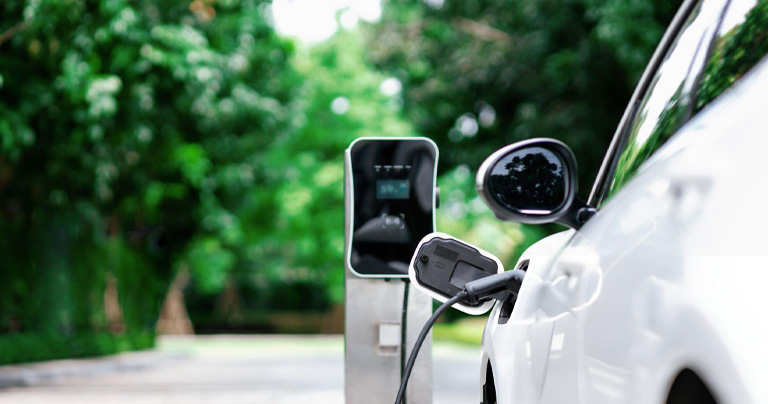
As concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability intensify, more people are seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprint. One of the most impactful changes individuals can make is switching from a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle to an electric vehicle (EV). The environmental benefits of EVs are numerous and significant, contributing to a cleaner, greener future.
1. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Traditional vehicles powered by gasoline or diesel are major contributors to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which are a leading cause of global warming. EVs, on the other hand, produce zero tailpipe emissions. Even when considering the emissions from electricity generation, EVs typically have a smaller carbon footprint than ICE vehicles, especially in regions where the electricity grid is powered by renewable energy sources like hydro, wind, or solar.
2. Improved Air Quality
The absence of tailpipe emissions from EVs means a significant reduction in pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants are known to contribute to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as smog formation. By switching to EVs, we can improve air quality, particularly in urban areas where vehicle density is high, leading to better public health outcomes.
3. Decreased Dependence on Fossil Fuels
EVs help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which are finite resources and often sourced from geopolitically unstable regions. By shifting to electricity, which can be generated from a variety of renewable sources, we can enhance energy security and reduce the economic and environmental costs associated with oil extraction, transportation, and refining.
4. Lower Noise Pollution
Electric motors are inherently quieter than internal combustion engines. This results in a reduction in noise pollution, which is particularly beneficial in densely populated areas. Lower noise levels can improve quality of life and have positive effects on mental health.
5. Enhanced Energy Efficiency
EVs are generally more energy-efficient than ICE vehicles. Electric motors convert a higher percentage of energy from the battery to drive the wheels, while ICEs waste a lot of energy as heat. This higher efficiency means that EVs can travel further on the same amount of energy, making better use of our resources.
6. Support for Renewable Energy Integration
The widespread adoption of EVs can complement the growth of renewable energy. EVs can act as distributed energy storage systems, helping to balance supply and demand on the grid. For example, EV batteries can be charged during periods of high renewable energy production and potentially provide power back to the grid during peak demand times, a concept known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G).
7. Reduced Life Cycle Environmental Impact
While the production of EVs, particularly the batteries, does have environmental impacts, studies have shown that over the entire life cycle, EVs are still less environmentally damaging than ICE vehicles. Innovations in battery recycling and the development of more sustainable battery materials are expected to further decrease the environmental impact of EV manufacturing.
Conclusion
Switching to an electric vehicle offers numerous environmental benefits, from reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution to decreasing dependence on fossil fuels and supporting renewable energy integration. As technology advances and the adoption of EVs increases, these benefits will only grow, contributing to a more sustainable and healthier future for all. By making the switch to an EV, individuals can play a crucial role in addressing climate change and promoting environmental stewardship.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Categories
- Car News (4)
- Car Reviews (3)
- Electric Cars (2)
- EV Battery (1)
- EV Charging (3)
- EV Testing (1)
- Uncategorized (1)
Recent Posts
Related posts


How to Maximize Your Electric Car's Battery Life